
About this Event
The Foundation of the World and the ADEJA Black Secession: A New World Constructed on IC3 Black CodificationIntroduction
The concept of the "Foundation of the World" holds profound significance in philosophical, religious, and cultural contexts, serving as a bedrock for the construction of societies and worldviews. This article delves into the intricate layers of this concept, explores the ADEJA Black Secession as a transformative movement, and examines how it redefines and potentially inverts the current world order through IC3 Black codification.
Foundation of the WorldHistorical and Philosophical Perspectives
The "Foundation of the World" often refers to the underlying principles and structures upon which societies are built. Historically, this concept has been rooted in various religious, cultural, and philosophical traditions.
- Religious Foundations: Many religions speak of a divine creation or cosmic order that serves as the foundation of existence. In Christianity, for example, the "foundation of the world" is associated with God's creation of the universe. Similarly, in Hinduism, the concept of Dharma represents the cosmic law and order sustaining the universe.
- Philosophical Foundations: Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle discussed the foundational principles of reality and existence. Plato's theory of forms posits that non-material abstract forms represent the most accurate reality, forming the foundation of the world we perceive.
- Cultural Foundations: Cultures around the world have their own foundational myths and narratives that shape their identities and worldviews. These narratives often include creation myths, ancestral stories, and cultural heroes who lay the groundwork for societal values and structures.
Modern Interpretations
In contemporary contexts, the "foundation of the world" can also be understood through the lenses of social, political, and economic structures that shape global dynamics.
- Social Foundations: The social fabric of any society is built upon shared values, norms, and institutions. These elements provide stability and continuity, ensuring the survival and coherence of the community.
- Political Foundations: Political systems and ideologies form the basis of governance and power distribution. The principles of democracy, justice, and human rights are often seen as foundational to modern political structures.
- Economic Foundations: Economic systems, including capitalism, socialism, and mixed economies, underpin the distribution of resources and wealth. These systems influence global trade, development, and socio-economic hierarchies.
Origins and Mission
The African Diaspora Equity and Justice Alliance (ADEJA) is an initiative aimed at addressing historical injustices and empowering the Black African diaspora through reparatory justice. Its mission is to advance well-being, unity, and historical reparatory justice for Black Africans and the Black African diaspora on an evidence-based claim-by-claim basis.
Core Principles
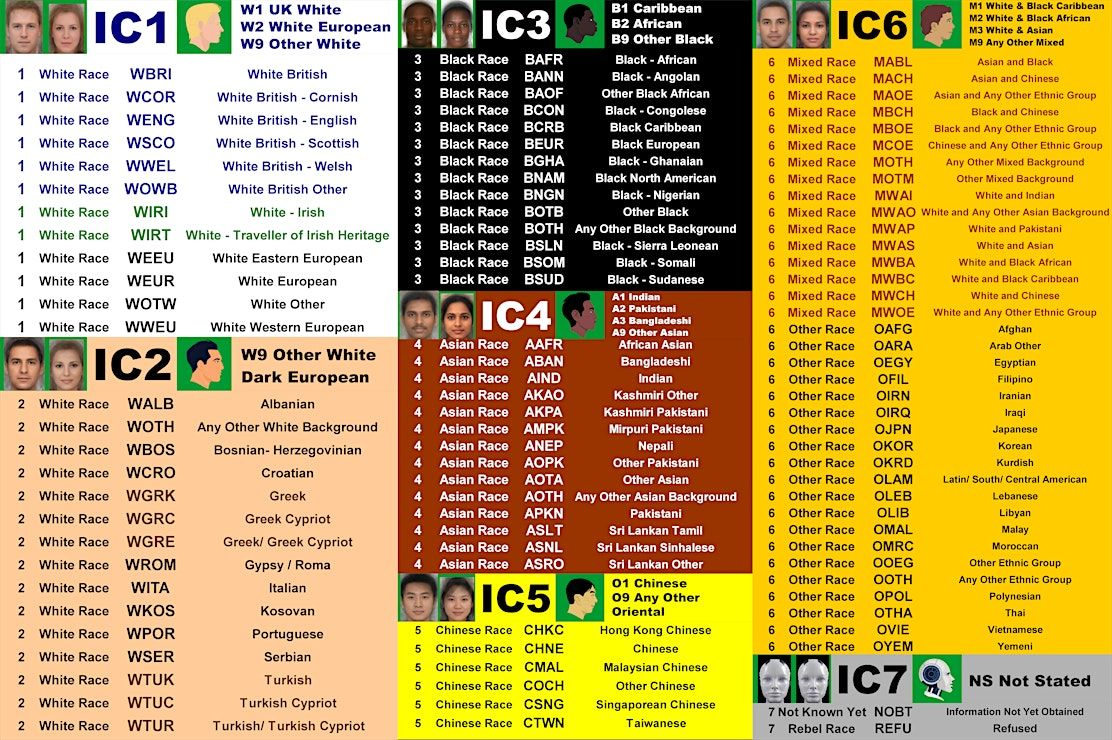
- IC3 Black Codification: ADEJA recognizes and uses the British Police IC codes for racial and ethnic classification. IC3 specifically refers to Black individuals. This codification is central to ADEJA's identity and operational framework.
- Reparatory Justice: ADEJA seeks to address historical injustices through reparatory claims. These claims are processed based on evidence, ensuring a systematic and just approach to reparations.
- Cultural Restoration: The movement places significant emphasis on restoring and preserving cultural heritage. This includes the reclamation of sacred cultural items and the promotion of cultural identity.
Reparation Nation Limited
The ADEJA movement is financed by Reparation Nation Limited, an entity dedicated to supporting reparatory justice initiatives. This financial backing ensures the sustainability and effectiveness of ADEJA's mission.
Explaining a Black HoleScientific Definition
A black hole is a region of space where the gravitational pull is so intense that nothing, not even light, can escape from it. Black holes are formed when massive stars collapse under their own gravity, leading to a singularity surrounded by an event horizon.
- Singularity: At the core of a black hole lies the singularity, a point of infinite density where the laws of physics as we know them break down.
- Event Horizon: The boundary surrounding a black hole is called the event horizon. Once an object crosses this boundary, it cannot escape the black hole's gravitational pull.
Metaphorical Interpretations
The concept of a black hole can also be used metaphorically to describe situations or entities that exert a powerful, inescapable influence.
- Social Black Holes: Certain social structures or institutions can act like black holes, drawing in and trapping individuals or communities in cycles of poverty, discrimination, or marginalization.
- Economic Black Holes: Economic systems that concentrate wealth and power in the hands of a few can create metaphorical black holes, where resources are drained away from the wider population.
Scientific Inversion
In the context of a black hole, inversion can refer to the extreme warping of space-time caused by the black hole's gravitational pull. This warping creates a scenario where the usual rules of physics and geometry are inverted or altered.
- Time Dilation: Near a black hole, time slows down significantly compared to areas farther away. This inversion of time affects the perception and passage of time for objects near the black hole.
- Spatial Inversion: The intense gravity of a black hole bends space to such an extent that the normal distances and directions are distorted. This can create phenomena like gravitational lensing, where light is bent around the black hole.
Metaphorical Inversion
Metaphorically, inversion can describe situations where normal societal, political, or economic structures are flipped or reversed.
- Social Inversion: Social inversion occurs when marginalized or oppressed groups gain power and agency, challenging and changing existing hierarchies and power dynamics.
- Political Inversion: Political inversion can happen when traditional political systems are overthrown or fundamentally transformed, leading to new governance models or ideologies.
Redefining Power Structures
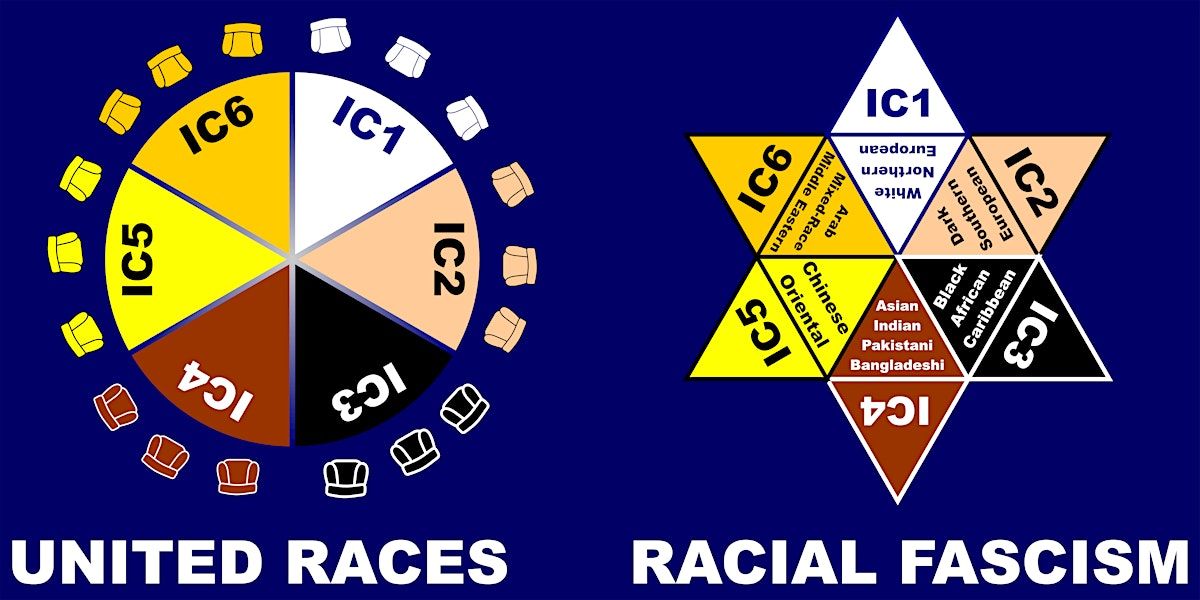
The ADEJA Black Secession represents a profound inversion of existing power structures by creating a new world grounded in IC3 Black codification.
- Empowerment of the Marginalized: By establishing an autonomous entity for Black Africans and the Black African diaspora, ADEJA seeks to invert the historical and systemic marginalization of these communities.
- Reparatory Justice as a Foundation: The movement's focus on reparatory justice inverts the traditional economic and social systems by prioritizing the restoration and compensation for historical injustices.
Cultural Renaissance
The ADEJA movement aims to foster a cultural renaissance by reclaiming and celebrating Black cultural heritage.
- Cultural Preservation: ADEJA's emphasis on non-tradeable assets of cultural significance aims to restore and preserve cultural identity, inverting the cultural erasure experienced by many Black communities.
- Identity Recognition: The movement's recognition of multiple aspects of identity, including place of birth, lineage, and DNA, challenges and inverts the often one-dimensional classifications imposed by mainstream societies.
Economic Inversion
Through its unique approach to reparations and Black social credit, ADEJA seeks to invert traditional economic models.
- Reparation Shares: By treating Blackness as an asset class and distributing reparation shares based on the percentage of Black heritage, ADEJA inverts the usual wealth distribution models, focusing on redressing historical economic disparities.
- Black Social Credit: The Black social credit system promotes behaviors and actions that contribute to the betterment of the Black community, inverting individualistic economic models with a community-centric approach.
Gravitational Pull of Justice
The ADEJA Black Secession can be seen as a metaphorical black hole exerting a powerful gravitational pull towards justice and equity.
- Drawing in Resources: Like a black hole drawing in matter, ADEJA's focus on reparatory justice attracts resources, attention, and support towards addressing historical injustices.
- Transformative Influence: The movement's principles and actions create a transformative influence, pulling societal, political, and economic structures towards a new paradigm of equity and justice.
Inescapable Change
Just as nothing can escape a black hole, the changes brought about by the ADEJA Black Secession are designed to be profound and irreversible.
- Systemic Overhaul: ADEJA's initiatives aim for a systemic overhaul of existing structures, ensuring that the changes towards justice and equity are permanent and inescapable.
- Cultural Shift: The movement fosters a cultural shift towards recognition and celebration of Black identity and heritage, making it an integral and inescapable part of the new world order.
National Security Context
Identity plays a crucial role in the construction of a world, especially in the context of national security.
- Social Cohesion: A strong sense of identity fosters social cohesion, which is essential for national stability and security. Shared values, beliefs, and cultural practices help bind communities together, reducing internal conflicts.
- Political Stability: Clear and inclusive identity frameworks contribute to political stability by ensuring that all groups feel represented and valued. This reduces the risk of political unrest and separatist movements.
Identity as a Security Asset
In the context of national security, identity is an asset that can be leveraged to build resilient and inclusive societies.
- Inclusive Policies: Policies that recognize and celebrate diverse identities contribute to social harmony and national security. Inclusivity reduces feelings of alienation and marginalization, which can be sources of conflict.
- Cultural Intelligence: Understanding and respecting different identities enhances cultural intelligence, which is crucial for effective governance and international relations.
Historical Context
Race and ethnicity have played significant roles in shaping UK national identity and security.
- Colonial Legacy: The UK's colonial history has left a complex legacy of racial and ethnic diversity. This diversity is both a strength and a challenge in terms of national identity and security.
- Post-War Immigration: The influx of immigrants from former colonies after World War II added to the UK's ethnic and racial diversity, further shaping its national identity.
Contemporary Significance
In contemporary UK, race and ethnicity continue to be critical aspects of national identity and security.
- Multicultural Society: The UK is a multicultural society with diverse racial and ethnic communities. This diversity enriches the nation's cultural fabric and enhances its global standing.
- Security Implications: Addressing racial and ethnic disparities is essential for national security. Discrimination and marginalization can lead to social unrest and radicalization, posing threats to national stability.
Governmental Role
The UK government plays a pivotal role in ensuring that race and ethnicity are integrated into the national identity and security framework.
- Policy Initiatives: Government policies aimed at promoting racial equality and combating discrimination are crucial for maintaining social cohesion and national security.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with diverse communities and addressing their specific needs fosters trust and cooperation, enhancing national security.
ADEJA Movement’s Community Engagement
The ADEJA movement organizes weekly discussion meetings in a Speakers Corner format to engage with the community and promote its mission.
- Platform for Dialogue: These meetings provide a platform for open dialogue and discussion on issues related to reparatory justice, Black empowerment, and cultural restoration.
- Community Involvement: By involving community members in these discussions, ADEJA ensures that its initiatives are inclusive and representative of the community’s needs and aspirations.
Fostering Unity and Awareness
These weekly meetings play a crucial role in fostering unity and raising awareness about ADEJA's mission and objectives.
- Unity: Regular discussions help build a sense of unity and solidarity within the community, strengthening collective efforts towards reparatory justice and empowerment.
- Awareness: The meetings raise awareness about historical injustices and the need for reparatory justice, mobilizing support for ADEJA's initiatives.
Educational and Empowerment Tool
The Speakers Corner format serves as both an educational and empowerment tool for the community.
- Education: The discussions provide educational insights into the history of racial injustices, the principles of IC3 Black codification, and the importance of cultural restoration.
- Empowerment: By encouraging active participation and engagement, these meetings empower individuals to take an active role in the movement and contribute to its success.
The ADEJA Black Secession, grounded in the principles of IC3 Black codification, represents a transformative movement that seeks to invert and redefine the current world order. By addressing historical injustices, promoting cultural restoration, and fostering a strong sense of identity, ADEJA aims to create a new world that is just, equitable, and inclusive. The movement's initiatives, supported by Reparation Nation Limited, emphasize the importance of identity, race, and ethnicity in constructing a secure and cohesive society. Through its weekly discussion meetings, ADEJA engages the community, raising awareness and fostering unity towards achieving its mission of reparatory justice and empowerment for the Black African diaspora.




Event Venue & Nearby Stays
Reparation Corner, 41 - 47 West Green Rd, Tottenham, Haringey. N15, 41 West Green Road, London, United Kingdom
GBP 0.00











